The location through which any PC speaks with our PC is basically called a Web Convention Address or IP address. For instance, if we need to stack a site page or download something, we require the location to convey that specific record or website page. That address is called an IP Address.
There are two forms of IP: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is the more seasoned form, while IPv6 is the fresher one. Both have their own elements and capabilities, however they vary in numerous ways. Understanding these distinctions assists us with seeing the reason why we really want IPv6 as the web develops and advances.
What is IP?
An IP, or Web Convention address, is a one of a kind arrangement of numbers relegated to every gadget associated with an organization, similar to the Web. It resembles a location for your PC, telephone, or some other gadget, permitting them to speak with one another. At the point when you visit a site, your gadget utilizes the IP address to find and interface with the site's server.
Types of IP Addresses
- IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
- IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
What is IPv4?
IPv4 addresses consist of two things: the network address and the host address. It stands for Internet Protocol version four. It was introduced in 1981 by DARPA and was the first deployed version in 1982 for production on SATNET and on the ARPANET in January 1983.
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit integers that have to be expressed in Decimal Notation. It is represented by 4 numbers separated by dots in the range of 0-255, which have to be converted to 0 and 1, to be understood by Computers. For Example, An IPv4 Address can be written as 189.123.123.90.
IPv4 Address Format
IPv4 Address Format is a 32-bit Address that comprises binary digits separated by a dot (.).
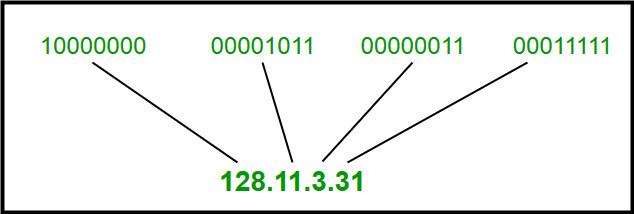
IPv4 Address Format
Drawback of IPv4
- Limited Address Space: IPv4 has a limited number of addresses, which is not enough for the growing number of devices connecting to the internet.
- Complex Configuration: IPv4 often requires manual configuration or DHCP to assign addresses, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Less Efficient Routing: The IPv4 header is more complex, which can slow down data processing and routing.
- Security Issues: IPv4 does not have built-in security features, making it more vulnerable to attacks unless extra security measures are added.
- Limited Support for Quality of Service (QoS): IPv4 has limited capabilities for prioritizing certain types of data, which can affect the performance of real-time applications like video streaming and VoIP.
- Fragmentation: IPv4 allows routers to fragment packets, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased chances of data being lost or corrupted.
- Broadcasting Overhead: IPv4 uses broadcasting to communicate with multiple devices on a network, which can create unnecessary network traffic and reduce performance.
What is IPv6?
IPv6 is based on IPv4 and stands for Internet Protocol version 6. It was first introduced in December 1995 by Internet Engineering Task Force. IP version 6 is the new version of Internet Protocol, which is way better than IP version 4 in terms of complexity and efficiency. IPv6 is written as a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:). It can be written as 128 bits of 0s and 1s.
IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 Address Format is a 128-bit IP Address, which is written in a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:).

IPv6 Address Format
To switch from IPv4 to IPv6, there are several strategies:
- Dual Stacking: Devices can use both IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time. This way, they can talk to networks and devices using either version.
- Tunneling: This method allows IPv6 users to send data through an IPv4 network to reach other IPv6 users. Think of it as creating a “tunnel” for IPv6 traffic through the older IPv4 system.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): NAT helps devices using different versions of IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) to communicate with each other by translating the addresses so they understand each other.
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 has a 32-bit address length | IPv6 has a 128-bit address length |
| It Supports Manual and DHCP address configuration | It supports Auto and renumbering address configuration |
| In IPv4 end to end, connection integrity is Unachievable | In IPv6 end-to-end, connection integrity is Achievable |
| It can generate 4.29×109 address space | The address space of IPv6 is quite large it can produce 3.4×1038 address space |
| The Security feature is dependent on the application | IPSEC is an inbuilt security feature in the IPv6 protocol |
| Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal | Address representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal |
| Fragmentation performed by Sender and forwarding routers | In IPv6 fragmentation is performed only by the sender |
| In IPv4 Packet flow identification is not available | In IPv6 packet flow identification are Available and uses the flow label field in the header |
| In IPv4 checksum field is available | In IPv6 checksum field is not available |
| It has a broadcast Message Transmission Scheme | In IPv6 multicast and anycast message transmission scheme is available |
| In IPv4 Encryption and Authentication facility not provided | In IPv6 Encryption and Authentication are provided |
| IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. | IPv6 has a header of 40 bytes fixed |
| IPv4 can be converted to IPv6 | Not all IPv6 can be converted to IPv4 |
| IPv4 consists of 4 fields which are separated by addresses dot (.) | IPv6 consists of 8 fields, which are separated by a colon (:) |
| IPv4’s IP addresses are divided into five different classes. Class A , Class B, Class C, Class D , Class E. | IPv6 does not have any classes of the IP address. |
| IPv4 supports VLSM(Variable Length subnet mask). | IPv6 does not support VLSM. |
| Example of IPv4: 66.94.29.13 | Example of IPv6: 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB |
Benefits of IPv6 over IPv4
The recent Version of IP IPv6 has a greater advantage over IPv4. Here are some of the mentioned benefits:
- Larger Address Space: IPv6 has a greater address space than IPv4, which is required for expanding the IP Connected Devices. IPv6 has 128 bit IP Address rather and IPv4 has a 32-bit Address.
- Improved Security: IPv6 has some improved security which is built in with it. IPv6 offers security like Data Authentication, Data Encryption, etc. Here, an Internet Connection is more Secure.
- Simplified Header Format: As compared to IPv4, IPv6 has a simpler and more effective header Structure, which is more cost-effective and also increases the speed of Internet Connection.
- Prioritize: IPv6 contains stronger and more reliable support for QoS features, which helps in increasing traffic over websites and increases audio and video quality on pages.
- Improved Support for Mobile Devices: IPv6 has increased and better support for Mobile Devices. It helps in making quick connections over other Mobile Devices and in a safer way than IPv4.
Conclusion
In simple terms, IPv4 and IPv6 are two versions of Internet Protocol addresses used to identify devices on a network. IPv6 is the newer version and offers many improvements over IPv4, such as a much larger address space, better security, and more efficient routing. However, IPv4 is still widely used, and the transition to IPv6 is ongoing. The main difference is that IPv6 can handle many more devices, which is crucial as the number of internet-connected devices continues to grow.
Frequently Asked Questions on Differences between IPv4 and IPv6 – FAQs
Which is Better IPv4 or IPv6?
IPv6 is better than IPv4 as IPv6 is more advanced and has more features than IPv4.
Can we use both IPv4 and IPv6
Yes, We can use both IPv4 and IPV6 in a single machine. There are devices that support dual addressing. When two devices communicate, they agree on which IP Version to use.
Which is faster IPv4 or IPv6?
Generally, IPv6 is faster than IPv4. However, when we go to a larger packet size, IPv6 can be slow in some cases.
